Memory Mapped File (MMF),内存映射文件。该技术将一个文件或者其他对象映射到进程的地址空间(虚拟内存),实现文件磁盘地址和进程虚拟地址空间中的一段虚拟地址的一一映射关系。
为什么要使用MMF?
MMF可以提高I/O性能,特别是对于大文件来说。
因为常规文件操作需要从磁盘到页缓存再到用户主存的两次数据拷贝。而mmap操控文件,只需要从磁盘到用户主存的一次数据拷贝过程。说白了,mmap的关键点是实现了用户空间和内核空间的数据直接交互而省去了空间不同数据不通的繁琐过程。因此mmap效率更高。
这里涉及一些操作系统的一些原理。
- 进程的概念
- 内核空间和用户空间
- 系统调用(system call)
- 内存管理,分页,分段
有时间整理下。
从网上扒的两张图:
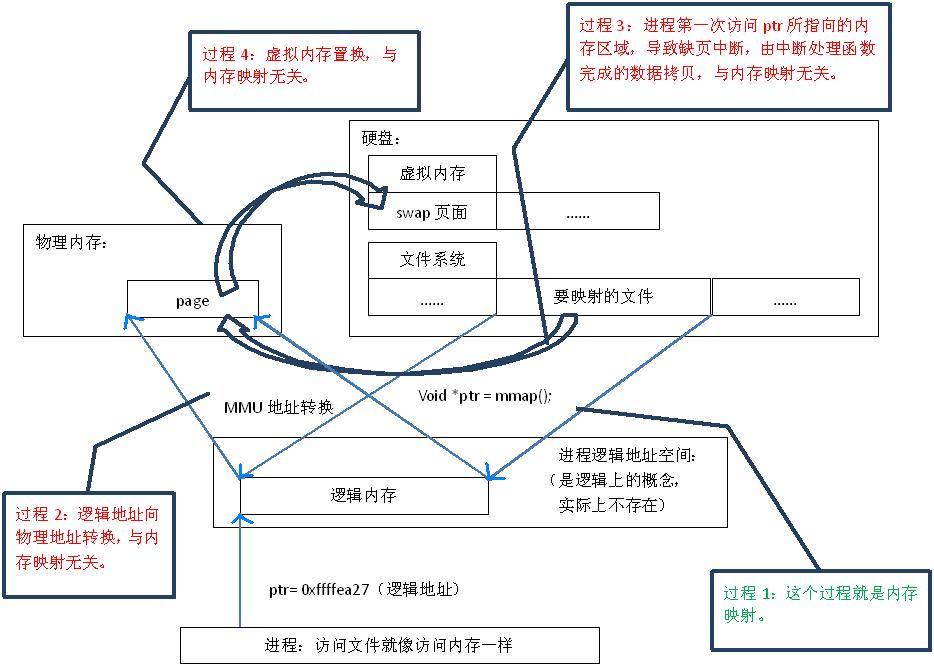
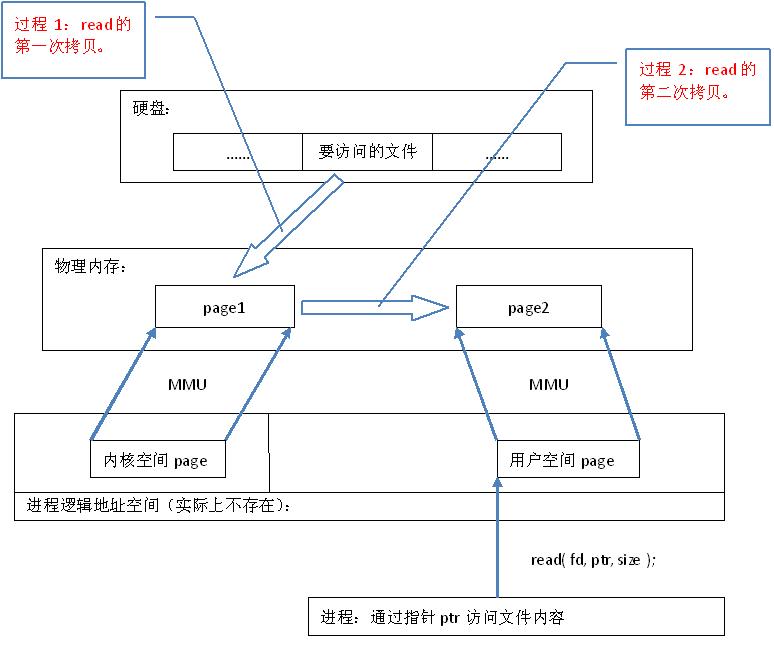
.NET中的MemoryMappedFile API
根据MSDN的说法,MMF分为两种情况:
- 持久化的MMF
- 持久化的MMF是与磁盘上的文件相关,调用
MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile方法创建的。当最后一个进程完成操作MMF操作之后,操作系统会将修改写回磁盘中。这个方式特别适合操作特别大的文件。
- 持久化的MMF是与磁盘上的文件相关,调用
- 非持久化的MMF
- 这种MMF不与磁盘上的文件相关联,调用
MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew方法创建的。当最后一个进程使用完毕之后,映射到内存的MMF被垃圾回收机制回收。这种方式适合用于多个进程之间通信(IPC)。
- 这种MMF不与磁盘上的文件相关联,调用
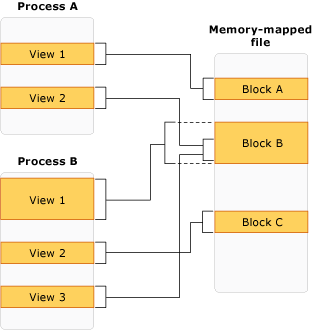
.Net framework中MMF的API
创建MMF对象
MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile : 创建持久化MMF
MemoryMappedFile.CreateNew:创建非持久化MMF
创建View对象
MemoryMappedViewAccessor: ramdom access view,适合与持久化MMF一起使用
MemoryMappedViewStream: sequence access view,适合与非持久MMF或IPC
使用上一步创建的view对象进行读写
Dispose View对象和MMF对象
摘自MSDN:
Memory-mapped files can be shared across multiple processes. Processes can map to the same memory-mapped file by using a common name that is assigned by the process that created the file.
To work with a memory-mapped file, you must create a view of the entire memory-mapped file or a part of it. You can also create multiple views to the same part of the memory-mapped file, thereby creating concurrent memory. For two views to remain concurrent, they have to be created from the same memory-mapped file.
Multiple views may also be necessary if the file is greater than the size of the application’s logical memory space available for memory mapping (2 GB on a 32-bit computer).
There are two types of views: stream access view and random access view. Use stream access views for sequential access to a file; this is recommended for non-persisted files and IPC. Random access views are preferred for working with persisted files.
Memory-mapped files are accessed through the operating system’s memory manager, so the file is automatically partitioned into a number of pages and accessed as needed. You do not have to handle the memory management yourself.
代码
写了一个简单的demo,来实现两个进程间通信。创建一个mmf.data文件,并由该文件创建MMF,Test1启动后检查该文件的某个字节,如果置位则退出。Test2进程启动后将MMF的这个直接置位。
Test1 进程:
1 | string filePath = @"mmf.data"; |
Test2进程:
1 | MemoryMappedFile mmf = MemoryMappedFile.OpenExisting("mmftest", MemoryMappedFileRights.ReadWrite); |
具体看这里:Github
windows提供的C++ API
其实.net framework中MMF的api只是对C++ api的封装。windows提供的API如下:
- CreateFileMapping
- OpenFileMapping
- MapViewOfFile
- MapViewOfFileEx
- UnmapViewOfFile
- FlushViewOfFile
- CloseHandle
具体参考 这里